Types of hearing loss and their consequences
Neurosensorial hearing loss: 90% of cases
Causes: Damage to the hair cells in the cochlea or to the auditory nerve, often due to aging or regular exposure to very loud sounds.
Neurosensorial hearing loss is irreversible but can often be helped with hearing aids.
Conductive hearing loss: 10% of cases
Causes: A foreign object, such as ear wax, blocking the ear canal, a perforated eardrum, malfunction of the ossicles, ear infection or fluid in the middle ear.
This type of hearing loss can often be resolved by medical intervention.
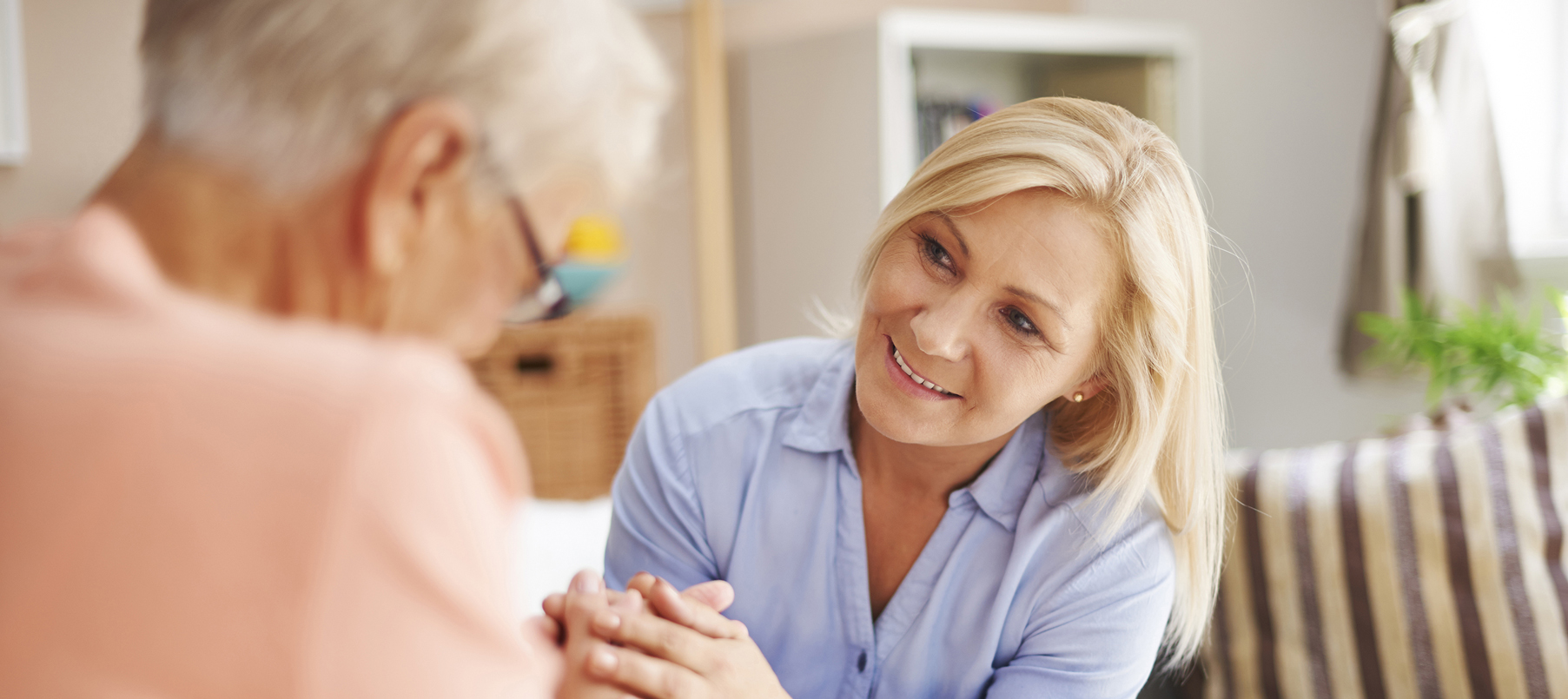
The consequences of hearing loss
Hearing loss has many effects, from emotional to physical:
- Isolation
- Embarrassment
- Frustration
- Lower self-esteem
- Fatigue
- Stress
- Decreased interest in work and less enjoyment of activities
- And more
Conversations with loved ones become challenging, work less interesting and activities less fun.
On the practical side, not hearing the stove timer, telephone, smoke alarm or traffic noise can affect our safety and sense of independence.
Reduced speech comprehension
Another impact of untreated hearing loss is the risk of sensory deprivation, which is when the lack of auditory stimulation leads to a reduced understanding of speech. Hearing loss is often irreversible, so delaying treatment makes it impossible to recover our full capacity for speech comprehension.
If you think you might have hearing loss, don’t wait!
Visit the “Health tips” section to learn about other types of hearing health issues that might be of interest.