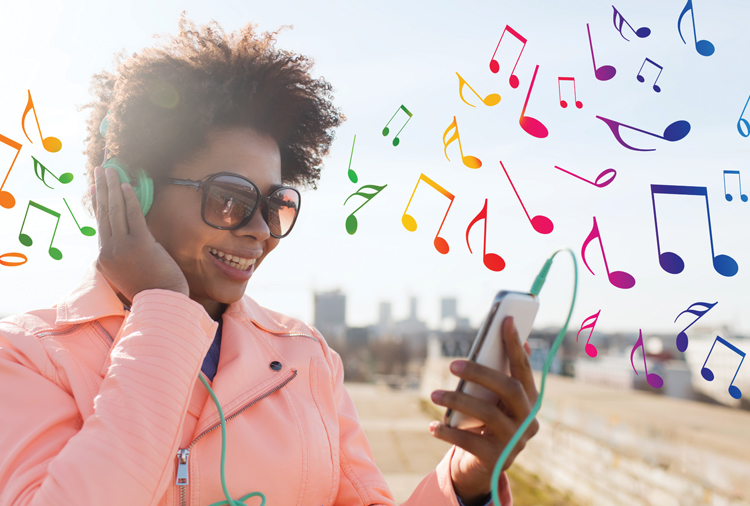
How music affects the brain
Music has a direct impact on our body. It makes us happy; it stimulates us. Several studies have observed the effects of music on the human brain. But which are they?
1. Music can influence our perception of effort or make us forget we’re tired
Music influences our perception of effort. According to a study by Southern Connecticut State University among female basketball players, those who listened to rhythmic music while exerting physical effort ran an average of five minutes longer than the others (at 85–90% of their maximum heartrate).
It makes us forget we’re tired, thus delaying the moment when we feel like we want to slow down. Music with a higher number of beats per minute (BPMs) can also increase an athlete’s speed, as shown in a study by sports psychologist Costas Karageorghis from Brunel University in the United Kindgdom.
It is fuel for an athlete. At the Peking Summer Olympics, where swimmer Michael Phelps racked up eight gold medals, he listened to the same song (I’m Me by rapper Lil Wayne) a few minutes before swimming. Phelps confided in an interview that he liked the enthusiasm of the delivery. Several studies have shown that music played before or during a sports performance has a positive effect for many reasons.
2. Listening to music releases dopamine in the brain
After much exploration of the brain, it has been shown that the zones that react to musical emotions are the same as those for all other emotions. So when we listen to music we like, the neural circuits that are activated are those that regulate motivation and reward. The limbic system is responsible for euphoric feelings, and is thus activated by drug addiction, but also by chocolate or extreme sports.
3. Improves sleep and relaxation
The calming effects of gentle music—instrumental or vocal—have been observed in people of all ages. According to clinical studies done among seniors, music therapy makes falling asleep easier, decreases night waking, improves sleep quality and increases the duration and effectiveness of the sleep.
4. Creates a feeling of well-being and positive emotions
Musical pieces have an expressive structure that is strong enough to inflict emotional states. Music can also reduce anxiety and stress and improve mood.
5. Background music stimulates creativity
- Helps develop cognitive skills like attention and memory.
- Facilitates creativity by helping us through difficult periods by creating an environment that is ripe for personal expression.
- Music evokes memories and associations. Listening to it in a relaxed, receptive state stimulates thoughts, images and feelings.
Experiment with the positive effects
- Pay attention to how certain types of music or songs affect your mood, your level of inspiration or your energy.
- Play different tracks depending on the activities you’re doing and your needs at the time: relaxing, inspiring, motivating, etc.
- Obviously, adjust the volume appropriately and in light of the circumstances.
The diagram above is for informational purposes only.